In the previous article of the RBI Grade B 2024 Phase 1 syllabus, we have explained the subject-wise decoded syllabus of Reasoning, Quantitative Aptitude, English, and General Awareness. Now, it’s time to understand the RBI Grade B Phase 2 syllabus, allowing you to adapt your preparation strategy effectively.
In this article, we’ll explain the detailed RBI Grade B Phase 2 syllabus for each subject along with the link where you can download the syllabus in PDF. Alongside the syllabus, you’ll also find the important topics, types of questions, and the difficulty level of questions that are asked from each subject of Phase 2.
RBI Grade B Phase 2 Syllabus
The RBI Grade B Phase 2 comprises three papers:
Paper 1: Economic and Social Issues
Paper 2: Descriptive English (Writing Skills)
Paper 3: Finance and Management
Below, we have provided an overview of the syllabus for each paper of RBI Grade B Phase 2, allowing you to tailor your preparation strategy accordingly.
Syllabus for Economic and Social Issues (ESI)
Here is the detailed ESI syllabus for RBI Grade B Phase 2:
- Growth and Development – Measurement of growth: National Income and per capita income – Poverty Alleviation and Employment Generation in India – Sustainable Development and Environmental issues.
- Indian Economy – Economic History of India – Changes in Industrial and Labour Policy, Monetary and Fiscal Policy since reforms of 1991 – Priorities and recommendations of Economic Survey and Union Budget – Indian Money and Financial Markets: Linkages with the economy – Role of Indian banks and Reserve Bank in the development process – Public Finance – Political Economy – Industrial Developments in India- Indian Agriculture – Services sector in India.
- Globalization – Opening up of the Indian Economy – Balance of Payments, Export-Import Policy – International Economic Institutions – IMF and World Bank – WTO – Regional Economic Co-operation; International Economic Issues
- Social Structure in India – Multiculturalism – Demographic Trends – Urbanisation and Migration – Gender Issues.
Click here to Download the RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI Syllabus in PDF.
Here is a video explaining the ESI Syllabus for the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Exam.
PYQ Analysis of RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI
Below is the analysis of objective and subjective questions of RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI:
Economic and Social Issues: Objective PYQ Analysis
We have analysed the year-wise trend of the number of objective questions asked from each Economic and Social Issues topic to help you identify the most important objective topics and the difficulty level.
| ESI Analysis (Objective) | |||||
| Economics | Social Issues | ||||
| SNo. | Year | Total Questions | Total Marks | Total Questions | Total Marks |
| 1 | 2023 | 9 | 17 | 21 | 33 |
| 2 | 2022 | 11 | 21 | 19 | 29 |
| 3 | 2021 | 22 | 37 | 8 | 13 |
| 4 | 2019 | 52 | 80 | 13 | 20 |
| ESI Topic-Wise Analysis (Objective) | |||
| Total Marks | |||
| SNo. | Topics | 2023 | 2022 |
| 1 | Government Schemes | 14 | 30 |
| 2 | Reports | 6 | 6 |
| 3 | General ESI Current Affairs | 16 | 14 |
| 4 | Statics | 14 | 0 |
Economic and Social Issues: Subjective PYQ Analysis
We have analysed the year-wise trend of the number of subjective questions asked from each topic of Economic and Social Issues to help you identify the most important subjective topics and the difficulty level.
| ESI Analysis Phase 2 (Subjective) | |||||
| Subject | Economics | Social Issues | |||
| SNo. | Year | Total Questions | Total Marks | Total Questions | Total Marks |
| 1 | 2023 | 3 | 30 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | 1 | 15 | 2 | 30 | |
| 3 | 2022 | 2 | 30 | 1 | 15 |
| 4 | 2 | 20 | 1 | 10 | |
| ESI Topic-Wise Analysis (Subjective) | |||
| Total Marks | |||
| SNo. | Topics | 2023 | 2022 |
| 1 | Sustainable Development and Environmental Issues | 15 | 0 |
| 2 | Urbanisation and Migration | 15 | 15 |
| 3 | Gender Issues | 15 | 0 |
| 4 | Industrial Developments in India | 10 | 0 |
| 5 | Monetary Policy since Reforms of 1991 | 10 | 10 |
| 6 | Poverty Alleviation and Employment Generation | 10 | 0 |
| 7 | Financial System | 0 | 15 |
| 8 | Economic History of India | 0 | 15 |
| 9 | Indian Money and Financial Markets | 0 | 15 |
| 10 | Social Sectors in India | 0 | 10 |
After analysing the number of questions asked from each topic of Economic and Social Issues in the past years, we have identified the important objective and subjective topics.
Important ESI Topics for RBI Grade B Phase 2
Based on our analysis, here are the most important ESI topics:
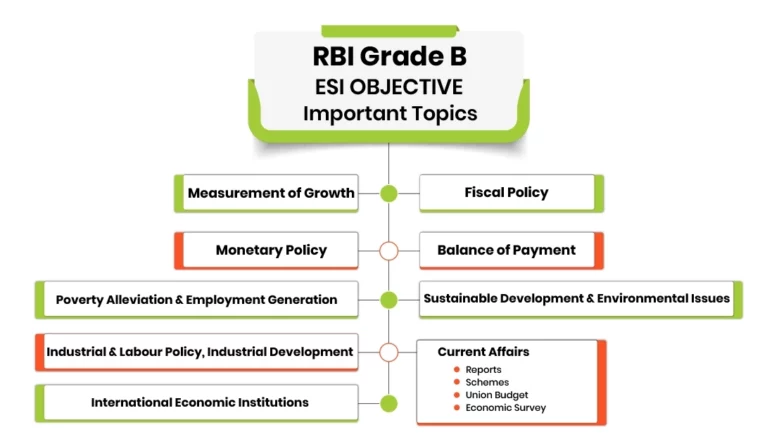
ESI (Objective)
Here are the most important topics for the ESI objective:
- Measurement of Growth
- Fiscal Policy
- Monetary Policy
- Balance of Payment
- Poverty Alleviation & Employment Generation
- Sustainable Development & Environmental Issues
- Industrial & Labour Policy, Industrial Development
- International Economic Institutions
- Current Affairs
- Reports
- Schemes
- Union Budget
- Economic Survey
ESI (Subjective)
Here are some of the important chapters based on the previous years’ question papers analysis:
- Growth and Development – Poverty Alleviation and Employment Generation in India – Sustainable Development and Environmental Issues.
- Indian Economy –Monetary Policy– Priorities and Recommendations of Economic Survey and Union Budget – Industrial Developments in India- Indian Agriculture.
- Globalization –Export-Import Policy
- Social Structure in India – Multiculturalism – Demographic Trends – Urbanisation and Migration – Gender Issues – Social Justice; Positive Discrimination in favour of the underprivileged – Social Movements – Indian political System – Human Development – Social Sectors in India, Health and Education.
Here is a video on important chapters & topics of ESI RBI Grade B.
After understanding the important topics, let’s take a look at their difficulty level.
RBI Grade B Phase 2 Economic and Social Issues Difficulty Level
Below is the objective and subjective difficulty level of RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI:
Economic and Social Issues Phase 2 Objective Difficulty Level
The table below contains the year-wise distribution of easy, moderate, and difficult questions out of the total number of objective Economic and Social Issues questions from 2019 to 2023. Understanding the difficulty level of questions helps you tailor your approach, prioritise topics, and fine-tune your preparation strategy.
| Economic and Social Issues Difficulty Level (Objective) | |||||
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2019 | ||
| Total Questions | 30 | 30 | 30 | 65 | |
| Difficulty Level | Easy | 6 | 9 | 9 | 22 |
| Moderate | 18 | 14 | 12 | 32 | |
| Difficult | 6 | 7 | 9 | 11 | |
Economic and Social Issues Phase 2 Subjective Difficulty Level
The table below contains the year-wise distribution of easy, moderate, and difficult questions out of the total number of subjective Economic and Social Issues questions from 2021 to 2023. Understanding the difficulty level of descriptive questions helps you tailor your answer writing approach to fine-tune your preparation strategy.
| Economic and Social Issues Difficulty Level (Subjective) | ||||
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||
| Total Questions | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Difficulty Level | Easy | 3 | 2 | 2 |
| Moderate | 0 | 2 | 2 | |
| Difficult | 3 | 2 | 2 | |
After getting familiar with the difficulty level, let’s understand the type of Economic and Social Issues questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2 exam.
Types of Economic and Social Issues Questions
Understanding the types of questions helps you identify the level and formats of Economic and Social Issues questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2. It ensures you are thoroughly prepared for all ESI question types encountered in the exam.
Below, we have explained the type of questions asked from each important topic of Economic and Social Issues in the RBI Grade B Phase 2:
ESI (Objective)
Below are the types of objective Economic and Social Issues questions asked in the exam.
1. Measurement of Growth
Question 1: Which of the following terms denotes the average income earned by a person in India?
- GDP per capita
- Per capita income
- Personal income
- Personal Disposable Income
- None of the above
Question 2: GDP deflator is defined as __________
- Nominal GDP multiplied by price level.
- Nominal GDP minus Real GDP.
- Nominal GDP divided by Consumer Price Index.
- Nominal GDP divided by Wholesale Price Index.
- Nominal GDP divided by real GDP.
2. Fiscal Policy
Question 1: In general context, which of the following is type of non-Tax revenue?
- GST
- Custom Duties
- Interest
- Production Duties
- None of the above
Question 2: Which of the following constitutes fiscal deficit?
- Total expenditure
- Revenue received – total expenditure
- Loan expenditure
- Total revenue received + Recovered loan and other receipt – Total Expenditure
- Total Borrowings
3. Monetary Policy
Question 1: Under the present Monetary Policy Framework Agreement signed on 20 February 2015, the RBI will be responsible for containing inflation targets at ___________
- 4% (with a standard deviation of 0.5%)
- 6% (with a standard deviation of 1%)
- 4% (with a standard deviation of 1%)
- 4% (with a standard deviation of 2%)
- 2% (with a standard deviation of 4%)
Question 2: In the context of the terms ‘repo’ and ‘repo rate’, which of the following statements is/are correct?
- “Repo” means an instrument for borrowing funds by selling securities with an agreement to repurchase the securities on a mutually agreed future date at an agreed price which includes interest for the funds borrowed
- Repo is a money market instrument, which enables collateralized short-term borrowing
- Repo rate is the rate at which the Reserve Bank of India lends money to commercial banks in India.
- All of the above
- None of the above
4. Balance of Payment
Question 1: Which of the following is not accounted for in the capital account under Balance of Payments?
- Direct Investment
- External Commercial Borrowing
- Remittances and Grants
- Portfolio Investment
- All of the above are accounted for in the capital account under Balance of Payment
Question 2: The balance of payments is defined as ___________
- The difference between household spending and income
- The difference between government spending and income
- A measure of the value of economic transactions between residents of a country and the rest of the world
- The difference between inflation and unemployment
- None of the above
5. Poverty Alleviation & Employment Generation
Question 1: Poverty Gap is defined as___________________
- Difference between the poverty line and actual income level.
- Gap between rich and poor.
- Gap between developed nation and developing nation.
- Difference between the poverty line and median income level.
- None of the above
Question 2: Swarnajayanti Gram Swarozgar Yojana has been restructured and launched as_______?
- Deen Dayal Antyodaya Yojana – National Livelihoods Mission
- Pradhan Mantri Adarsh Gram Yojana
- Prime Minister’s Employment Generation Programme
- Mahatma Gandhi National Rural Employment Guarantee Scheme
- None of the above
6. Sustainable Development & Environmental Issues
Question 1: The report titled “World Resources Report: Creating a Sustainable Food Future” has been issued by which of the following organizations?
- World Bank
- UN Environment Programme
- UN Development Programme
- Both A and B
- All of the above
Question 2: As part of the 2030 Agenda for sustainable development, what is the total number of targets to be achieved under the 17 SDGs?
- 189
- 180
- 179
- 169
- 164
7. Industrial & Labour Policy, Industrial Development
Question 1: Recently the base year of the Index of Industrial Production was revised to 2011-12. Which among the following is/are the reason for revising the base year periodically?
- To capture structural changes in the economy
- To improve the quality, coverage, and representativeness of the IIP.
- To bring it in alignment with the base year of other macroeconomic indicators like the Gross Domestic Product (GDP) and Wholesale Price Index (WPI).
- All of the above
- None of the above
Question 2: Department of Industrial Policy & Promotion (DIPP) (now DPIIT) works under which of the following union ministries?
- Ministry of Finance
- Ministry of Heavy Industries and Public Enterprises
- Ministry of Micro, Small, and Medium Enterprises
- Ministry of Corporate Affairs
- Ministry of Commerce and Industry
8. International Economic Institutions
Directions: It is the only global international organization dealing with the rules of trade between nations. At its heart are its agreements, which have been negotiated and signed by the bulk of the world’s trading nations and ratified in their parliaments. The goal is to ensure that trade flows as smoothly, predictably and freely as possible. Its Secretariat is located in Geneva, Switzerland, and has an annual budget of approximately CHF 200 million.
From the early days of the Silk Road to the creation of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) and the birth of this organisation, trade has played an important role in supporting economic development and promoting peaceful relations among nations. Decisions in the organisation are generally taken by consensus of the entire membership.
Question 1: Which round of talks has resulted into the creation of the organisation mentioned in the given passage?
- Geneva Round
- Doha Round
- Uruguay round
- Bretton Woods Round
- Paris Round
Question 2: What is the establishment year of the organisation mentioned in the given passage?
- 1st October 1995
- 1st March 1985
- 1st July 1944
- 15th January 1975
- 1st January 1995
9. Current Affairs: Reports, Schemes, Union Budget, Economic Survey
Question 1: As per the Annual Report of RBI, Commercial banks remained the largest holders of government securities[including T-Bills and state government securities (SGSs)] accounting for __________ as at end-March 2023.
A. 27.5%
B. 37.5%
C. 25.5%
D. 31.5%
E. 28.5%
ESI (Subjective)
Below are the types of subjective Economic and Social Issues questions asked in the exam.
Question 1: Explain three government schemes related to poverty alleviation and employment generation. (400 words, 10 Marks)
Question 2: Discuss Monetary Policy and mention in brief at least eight Monetary Policy Instruments. (400 words, 10 Marks)
Question 3: What are the problems being faced by Startup entrepreneurs in tier 2 and 3 cities in India? (400 words, 10 Marks)
Question 4: In the context of UNDP’s Gender Equality Strategy 2022-25 and Gender Social Norms Index for promoting gender equality, what actions can India take toward gender sensitization? (600 words, 15 Marks)
Question 5: “Better migration policies for a prospering World”. Elaborate the statement in light of the recently released World Development Report 2023: Migrants, Refugees and Societies by the World Bank. Also, discuss key recommendations of the Report. (600 words, 15 Marks)
Question 6: In the light of the Report on Currency and Finance released by the RBI, explain:
A) Macroeconomic Effect of Climate Change
B) Three landmark global collaborations on climate change (600 words, 15 Marks)
Click here to Download the RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI PYQs in PDF.
Now that you have understood the types of ESI questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2, let’s learn the important books to prepare for the exam.
Important Books for RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI
Here are the important books that can help you cover the RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI syllabus.
| RBI Grade B Economics Books for Phase 2 Exam Preparation | |||
| Books | Author | Publisher | Buy Here |
| Indian Economy | Ramesh Singh | McGraw Hill | Buy Online |
| Indian Economy | V.K. Puri, S.K. Misra, Bharat Garg | Himalaya Publishing House | Buy Online |
Other Preparation Material
| RBI Grade B Social Books for Phase 2 Exam Preparation | |||
| Books | Author | Publisher | Buy Here |
| Social Problems in India | Ram Ahuja | Rawat | Buy Online |
| Sociology: Principles Of Sociology With An Introduction To Social Thoughts | C.N. Shankar Rao | S Chand | Buy Online |
Other Preparation Material
For current affairs:
- Reports: The Hindu ePaper
- Schemes: Press Information Bureau Government of India
- ESI Current Affairs: The Hindu ePaper
Here is a video on the best books for Economics and Social Issues for RBI Grade B.
After getting familiar with the important books, let’s understand the RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI preparation strategy.
How to Prepare for RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI
Follow these below-mentioned strategies to prepare for RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI:
1. Break the ESI syllabus
ESI is divided into 2 parts: Economic and Social Issues. Out of the total 100 marks, Economics holds a weightage of 40-45 marks, while Social Issues account for 55-60 marks.
2. Understand the ESI Format
ESI is divided into two parts: Objective and Subjective.
1. Objective:
It includes two parts: Static and Current Affairs. According to the previous years’ trends, the majority of questions are asked from current affairs such as Schemes, Reports, Union Budget, Economic Surveys, etc.
a. Static
For the static part, you should cover the important chapters such as:
- Inflation
- Balance of Payment
- Monetary Policy
- Fiscal Policy
- Measurement of Growth
- Sustainable Development and Environmental Issues
- International Economic Institutions
Important Note: When we refer to important topics, we mean that you should give these topics high priority, especially if you have time constraints. However, you should cover every topic mentioned in the RBI Grade B Phase 2 ESI Syllabus, especially social issues. Moreover, the questions asked from the static part are also influenced by current affairs. So, practise your static MCQs with respect to current affairs.
b. Current Affairs
The current affairs in the ESI section are divided into three categories:
- Schemes
- Reports
- Current Affairs
A comprehensive understanding of schemes, reports, and current affairs is crucial to excel in this paper. For e.g., in a previous year’s exam, RBI asked about “Adarsh Gram Yojana.” Below is the question.
“Question: Which among the following states was not included in the initial pilot phase of the scheme?”
To answer such questions accurately, it’s essential to have a thorough knowledge of the schemes and reports.
Moreover, the difficulty level of questions asked in the past years has increased, and there were some unexpected questions. For e.g., in 2023, questions are asked on topics such as the India-New Zealand Agreement and the World Bank’s Human Capital Index.
2. Subjective:
The exam has asked a combination of current and static questions over the past few years. First, you need to understand that the questions are not bookish. You will see application-based questions in the exams to evaluate your analytical ability.
Let’s take a look at the previously asked questions (2022) and understand how to approach these questions.
- What is meant by economic reforms? Explain all types of reform in economic policies in India from the 1990s till now.?
- What is NBFC? How is it different from a bank? Mention five types of NBFCs registered with RBI.
- Although Urbanization has been spreading to the hinterlands, Casts, and gender discrimination is rampant. In this opinion, how will you justify the protective discrimination policy?
- Rural entrepreneurship: How the hinterland’s young enterprises can solve India’s social challenges?
Now, the first two questions can be answered easily if you have thoroughly read “Economic Reforms” and “NBFC”. However, no book can help you write the next two questions. To answer these types of questions, you need to have a deep understanding of the topic and the ability to express your views in your own words effectively.
How to Score Good Marks in ESI Descriptive
Follow these 7 pillars and make a topic-wise folder.
- Reforms: Understand if any reforms have been done on a particular topic.
- Challenges: Remember the challenges faced in that topic.
- Current Developments: Get an idea of the current developments in that topic.
- Reports/Data/Facts: Understand the data and facts from reports. So, you can quote them in descriptive answers.
- Social, Economic, Legal, and Political Angles: Understand the social, economic, legal, and political agenda behind any specific initiative.
- Schemes: Understand the schemes regarding that topic.
- Example: Note the examples you can quote in your descriptive answer.
Here is a video explaining a step-by-step strategy for preparing ESI for the RBI Grade B exam.

Now that you have understood how to prepare for the RBI Phase 2 ESI, let’s understand the Descriptive English syllabus.
Syllabus for Descriptive English
There is no defined syllabus for Descriptive English, but as per the paper scheme, 3 questions are asked. These 3 questions are asked under the following topics-
- Essay: An essay is asked to be drafted out of 4-5 options (about 400 words).
- Precis Writing: Precis writing is to be done in about 140 words.
- Reading Comprehension: 4-5 questions based on reading comprehension are asked.
Click here to Download the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Descriptive English Syllabus in PDF.
PYQ Analysis of RBI Grade B Phase 2 Descriptive English
We have analysed the year-wise trend of the number of questions asked from Descriptive English from 2019 to 2023 to help you identify the most important topics and the difficulty level.
| Descriptive English PYQ Analysis Phase 2 | |||||
| Total Marks | |||||
| SNo. | Essay Topics | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2019 |
| 1 | Economics and Social Issues | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| 2 | Finance | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 3 | Current Affairs | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 4 | Management | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 |
After analysing the number of questions asked from each topic of Descriptive English in the past years, we have identified the important topics.
RBI Grade B Phase 2: Important Descriptive English Topics
Descriptive English questions can be asked from any of the above-mentioned essay topics. Therefore, it’s essential to cover ESI and Finance and Management syllabus and regularly follow reputable newspapers, news websites, official government portals, and magazines to stay informed about these current affairs topics.
After understanding the important topics, let’s take a look at their difficulty level.
RBI Grade B Phase 2 Descriptive English Difficulty Level
The table below contains the year-wise distribution of easy, moderate, and difficult questions out of the total number of Descriptive English essay questions from 2021 to 2023. Understanding the difficulty level of descriptive questions helps you tailor your answer writing approach to fine-tune your preparation strategy.
| Descriptive English Essay Difficulty Level Phase 2 | |||||
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2021 | ||
| Total Questions | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | |
| Difficulty Level | Easy | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Moderate | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | |
| Difficult | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | |
After getting familiar with the difficulty level, let’s understand the type of Descriptive English questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2 exam.
Types of Descriptive English Questions
Understanding the types of questions helps you identify the level and formats of Descriptive English questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2. It ensures that you are thoroughly prepared for all question types encountered in the exam.
Below, we have explained the type of questions asked from each topic of Descriptive English in the RBI Grade B Phase 2.
Question 1: Write an essay of about 600 words on any one of the following: (30 Marks)
1. Climate Change and its economic impacts on developing countries. (ESI Topic)
2. India’s own digital currency: E-rupee. (Finance topic)
3. Innovative motivation methods for modern employees aligned with organisation growth. (Management topic)
4. Multi-linguistic Social Media account for businesses – need? (Current Affairs)
Question 2: Make a precis of the following passage reducing it to about 180 words, and also, give it a suitable title. ( 30 Marks)
In what became the first celebration of International Women’s Day in 1911, more than a century ago, women worldwide gathered to fight for their right to education, work, vote, hold public office, and end discrimination. That same year, the first Model-T car rolled off the assembly line, and the ComputingTabulating-Recording Company was founded, later renamed IBM. Decades later, British mathematician Alan Turing would first question whether machines can think, and the term artificial intelligence (AI) was coined in 1956.
Women’s rights, their economic empowerment, and technology have advanced considerably in the last century. Advances in machine learning, large datasets, and increased computing power have driven AI development in recent years, moving from academic discussions into remarkable real-world applications with real opportunities and challenges for gender equality.
For many, 2022 was the year AI became real. The rise of foundation or general-purpose AI models, including the emergence of very large language models, paved the way for a “generative AI” renaissance, with AI that generates novel content, transposes text-to-video and -image, and offers advanced chatbots accessible to all. AI tools became mainstream with the release of AI model ChatGPT, which reached about 100 million monthly active users in just two months, making it the fastest-growing consumer application in history.
With AI tools already changing work, education, and leisure in significant ways, we must ask: is today’s AI addressing the gender equality issues that have plagued policy makers for decades? While women have gained the right to education, work, vote, hold public office and protection against gender discrimination, technologies play a big part in ensuring those rights are upheld. Are policy makers doing enough to ensure that today’s AI systems do not perpetuate yesterday’s biases?
Although technologies have evolved, some barriers to gender equality and economic empowerment are still much like the ones women faced over a century ago when the world celebrated the first International Women’s Day. In many countries, women still have less access to training, skills, and infrastructure for digital technologies. They are still underrepresented in AI research and development (R&D), while harmful stereotypes and biases embedded in algorithms continue to prompt gender discrimination and limit women’s economic potential.
Today, men are leading most cutting-edge AI companies, while female voices animate most Virtual Personal Assistants (VPAs) and advanced humanoid robots – like Alexa and Siri, or
robots Sophia, Ameca, Jia Jia, and Nadine. This reflects gender biases at home and in the workplace by reinforcing traditional norms of women as nurturers in supporting roles.
New generative AI tools can also produce overtly sexualised digital avatars or images of women while portraying men as more professional and career-oriented. As generative AI and robotics advance, their effects on women’s economic and social equality remain to be seen.
Question 3: Read the passage given below and answer the following questions on the basis of the passage in your own words.
Some economists argue that businesses are using the cost of living crisis as an opportunity to generate excessive profits. This isn’t just an idle theory. Economists at the European Central Bank (ECB) actually have some statistical evidence to back it up.
You can only learn so much by breaking down the consumer price index, the traditional measure of rising prices (inflation, let’s not forget, is simply the rate at which the prices of the average goods and services we spend most of our money on change each year). That might tell you how much is down to food price inflation but it can’t give you a sense of how much of that given increase in food prices is benefiting workers versus their employers.
Basic economic theory teaches that charging what the market can bear will prompt companies to produce more, constraining prices and ensuring that more people have access to the good that’s in short supply. Say you make empanadas, and enough people want to buy them that you can charge $5 each even though they cost only $3 to produce. That might allow you to invest in another oven so you can make more empanadas — perhaps so many that you can lower the price to $4 and sell enough that your net income.
Tempting as it is to blame businesses for what we’re suffering through, there’s not an enormous amount of evidence from these figures that they are the main culprit. Actually, taxes (in other words the government) contributed much more to inflation in 2021 and into 2022 than business profits. Now, with Britain facing double-digit inflation, a miserable cost of living crisis and rising interest rates, the above might not be of much consolation. And it’s quite possible the numbers may well shift – note that these figures are a little slow to be updated, so we don’t know the picture as of the early part of this year.
There is not much disagreement that many companies have marked up goods in excess of their own rising costs. This is especially evident in industries such as shipping, which had record profits as soaring demand for goods filled up boats, driving up costs for all traded goods. Across the economy, profit margins surged during the pandemic and remained elevated.
Even so, it’s a reminder that the data sometimes tells a subtly different story to the mainstream narrative.
1. How are businesses using the cost-of-living crisis to generate excessive profits?
2. What is the traditional measure of rising prices?
3. Why is the consumer price index not sufficient to understand the impact on workers and employers?
4. What has contributed more to inflation in recent years, business profits or taxes?
5. In which industries have companies marked up goods in excess of their rising costs?
Click here to Download the RBI Grade B Phase 2 English PYQs in PDF.
Now that you have understood the types of Descriptive English questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2, let’s learn the important books to prepare for the exam.
Important Books for RBI Grade B Phase 2 Descriptive English
It is not recommended to buy any separate books for Descriptive English as this part only tests the writing skills of candidates. They should read finance and banking-related articles in magazines and newspapers to improve their writing skills. They can improve their Descriptive English by watching multiple YouTube videos on the topics:
- Essay & Precis Writing
- Answer Writing Practice
- Reading Comprehension
- Tips To Write Descriptive Answers
Watch these videos, learn the basics, and start applying them by practising daily.
Other Preparation Material
- Press Information Bureau Government of India (for collecting important points for various topics)
- The Hindu ePaper (for building command over language)
After getting familiar with the important books, let’s understand the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Descriptive English preparation strategy.
How to Prepare for RBI Grade B Phase 2 Descriptive English
Follow these below-mentioned strategies to prepare for RBI Grade B Phase 2 Descriptive English:
1. Understand the Format
Get familiarised with the format of the Descriptive English section, which usually includes essays, precis, and reading comprehension. Learn the technicalities of these writing formats. For e.g.,
- Understand the difference between a precis and a summary.
- Determine whether a precis should include a heading or not.
- Decide whether to use the first or third forms while writing a precis.
2. Build a Strong Vocabulary
A rich vocabulary is crucial for expressing your ideas clearly. Read extensively and learn new words.
3. Improve Grammar and Punctuation
Brush up on your grammar skills and punctuation rules. Grammatical errors can impact the readability of your writing.
4. Practice Regularly
Read editorials from one financial and one non-financial newspaper and type (not write) answers in your own words because the exam is online.
Moreover, use Notepad to type instead of MS Word or Google Docs, as auto-correct is not available in Notepad, allowing you to accurately evaluate your mistakes and learn from them.
Check your mistakes (grammar, punctuation, spelling, etc.) on Grammarly.com.
5. Pay Attention to the Structure
Focus on the structure of essays and letters. Develop a captivating introduction, a detailed body, and a firm conclusion. Make sure your writing flows logically.
6. Develop Content
Understand your topic first and support your ideas with examples, facts, statistics, and relevant anecdotes.
7. Evaluate Yourself
Evaluating your content is crucial to identify your mistakes and areas of improvement.
Here is a video of RBI Grade B 2023 Descriptive English Syllabus preparation strategy.

Now that you have understood how to prepare for the RBI Phase 2 Descriptive English, let’s understand the Finance and Management syllabus.
Syllabus for Finance and Management
Here is the detailed General Finance and Management syllabus for RBI Grade B Phase 2:
a) Financial System
- Structure and Functions of Financial Institutions
- Functions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Banking System in India – Structure and Developments, Financial Institutions – SIDBI, EXIM Bank, NABARD, NHB, NaBFID etc.
- Recent Developments in the Global Financial System and its Impact on Indian Financial System
- Role of Information Technology in Banking and Finance
- Non-Banking System
- Developments in Digital Payments
b) Financial Markets
- Primary and Secondary Markets (Forex, Money, Bond, Equity, etc.), functions, instruments, and recent developments.
c) General Topics
- Financial Risk Management
- Basics of Derivatives
- Global financial markets and International Banking – broad trends and latest developments
- Financial Inclusion
- Alternate source of finance, private and social cost-benefit, Public-Private Partnership
- Corporate Governance in the Banking Sector
- The Union Budget – Concepts, approach and broad trends
- Basics of Accounting and Financial Statements – Balance Sheet, Profit and Loss, Cash Flow Statements, Ratio Analysis (such as Debt to Equity, Debtor Days, Creditor Days, Inventory Turnover, Return on Assets, Return on Equity, etc.)
- Inflation: Definition, trends, estimates, consequences and remedies (control): WPI- CPI – components and trends; striking a balance between inflation and growth through monetary and fiscal policies.
d) Management
- Fundamentals of Management & Organizational Behaviour: Introduction to management; Evolution of management thought: Scientific, Administrative, Human Relations and Systems approach to management; Management functions and Managerial roles; Nudge theory
- Meaning & concept of organizational behaviour; Personality: meaning, factors affecting personality, Big Five model of personality; concept of reinforcement; Perception: concept, perceptual errors. Motivation: Concept, importance, Content theories (Maslow’s need theory, Alderfers’ ERG theory, McCllelands’ theory of needs, Herzberg’s two factor theory) & Process theories (Adams equity theory, Vrooms expectancy theory).
- Leadership: Concept, Theories (Trait, Behavioural, Contingency, Charismatic, Transactional and Transformational Leadership; Emotional Intelligence: Concept, Importance, Dimensions. Analysis of Interpersonal Relationship: Transactional Analysis, Johari Window; Conflict: Concept, Sources, Types, Management of Conflict; Organizational Change: Concept, Kurt Lewin Theory of Change; Organizational Development (OD): Organisational Change, Strategies for Change, Theories of Planned Change (Lewin’s change model, Action research model, Positive model).
- Ethics at the Workplace and Corporate Governance: Meaning of ethics, why ethical problems occur in business. Theories of ethics: Utilitarianism: weighing social cost and benefits, Rights and duties, Justice and fairness, ethics of care, integrating utility, rights, justice and caring, an alternative to moral principles: virtue ethics, teleological theories, egoism theory, relativism theory, Moral issues in business: Ethics in Compliance, Finance, Human Resources, Marketing, etc. Ethical Principles in Business: introduction, Organization Structure and Ethics, Role of Board of Directors, Best Practices in Ethics Programme, Code of Ethics, Code of Conduct, etc.
- Corporate Governance: Factors Affecting Corporate Governance; Mechanisms of Corporate Governance
- Communication: Steps in the Communication Process; Communication Channels; Oral versus Written Communication; Verbal versus non-verbal Communication; upward, downward and lateral communication; Barriers to Communication, Role of Information Technology.
Here is a video of the Finance and Management syllabus for the RBI Grade B Phase 2 exam.
Click here to Download the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management Syllabus in PDF.
PYQ Analysis of RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management
Below is the objective and subjective analysis of RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management:
Finance and Management Objective PYQ Analysis Phase 2
We have analysed the year-wise trend of the number of objective questions asked from each topic of Finance and Management from 2019 to 2023 to help you identify the most important objective topics and the difficulty level.
| General Finance and Management Analysis Phase 2 (Objective) | |||||
| Subject | Finance | Management | |||
| SNo. | Year | Total Questions | Total Marks | Total Questions | Total Marks |
| 1 | 2023 | 16 | 26 | 14 | 24 |
| 2 | 2022 | 12 | 19 | 18 | 31 |
| 3 | 2021 | 16 | 29 | 14 | 21 |
| 4 | 2019 | 35 | 52 | 30 | 48 |
| Finance Topic-Wise Analysis Phase 2 (Objective) | ||||
| Total Marks | ||||
| SNo. | Topics | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 |
| 1 | Fiscal Policy | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Alternate Source of Finance | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | Forex Markets | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 4 | Ratios | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 5 | Financial Institutions | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 6 | Corporate Governance in Banking Sector | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| 7 | Financial Inclusion | 10 | 0 | 0 |
| 8 | Banking and Financial System | 0 | 6 | 0 |
| 9 | Primary and Secondary Markets | 0 | 8 | 13 |
| 10 | Current | 0 | 5 | 0 |
| 11 | Changing Landscape in Banking Sector | 0 | 0 | 1 |
| 12 | FinTech | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| 13 | Union Budget | 0 | 0 | 3 |
| 14 | PPP | 0 | 0 | 6 |
| Management Topic-Wise Analysis Phase 2 (Objective) | ||||
| Total Marks | ||||
| SNo. | Topics | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 |
| 1 | Leadership | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | Corporate Governance | 2 | 8 | 0 |
| 3 | Motivation | 6 | 6 | 4 |
| 4 | Communication | 6 | 7 | 5 |
| 5 | Ethics | 2 | 1 | 0 |
| 6 | Personality and Perception | 1 | 1 | 1 |
| 7 | Emotional Intelligence and Interpersonal Behavior | 1 | 0 | 1 |
| 8 | General Management | 2 | 1 | 1 |
| 9 | Fundamental of Organisational Behavior | 0 | 6 | 4 |
| 10 | Organisational Change | 0 | 1 | 5 |
Finance and Management Subjective PYQ Analysis Phase 2
We have analysed the year-wise trend of the number of subjective questions asked from each topic of Finance and Management to help you identify the most important subjective topics and the difficulty level.
| General Finance and Management Analysis Phase 2 (Subjective) | |||||
| Subject | Finance | Management | |||
| SNo. | Year | Total Questions | Total Marks | Total Questions | Total Marks |
| 1 | 2023 | 1 | 15 | 2 | 30 |
| 2 | 2 | 20 | 1 | 10 | |
| 3 | 2022 | 1 | 15 | 2 | 30 |
| 4 | 2 | 20 | 1 | 10 | |
| Finance and Management Topic-Wise Analysis Phase 2 (Subjective) | ||||
| Total Marks | ||||
| SNo. | Topics | 2023 | 2022 | 2021 |
| 1 | Personality & Perception | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| 2 | General Management | 15 | 0 | 0 |
| 3 | Ethics | 10 | 10 | 0 |
| 4 | Current Affairs | 35 | 10 | 0 |
| 5 | FinTech | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 6 | Organization Change | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 7 | Communication | 0 | 15 | 0 |
| 8 | Global Financial Crisis | 0 | 10 | 0 |
| 9 | Concept of Reinforcement | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 10 | Corporate Governance | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 12 | Leadership | 0 | 0 | 10 |
| 13 | Risk Management | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 14 | Financial Institutions | 0 | 0 | 15 |
| 15 | Union Budget | 0 | 0 | 10 |
After analysing the number of questions asked from each topic of Finance and Management in the past years, we have identified the important objective and subjective topics.
RBI Grade B Phase 2: Finance and Management Important Topics
Based on our analysis, here are the most important Finance and Management topics:
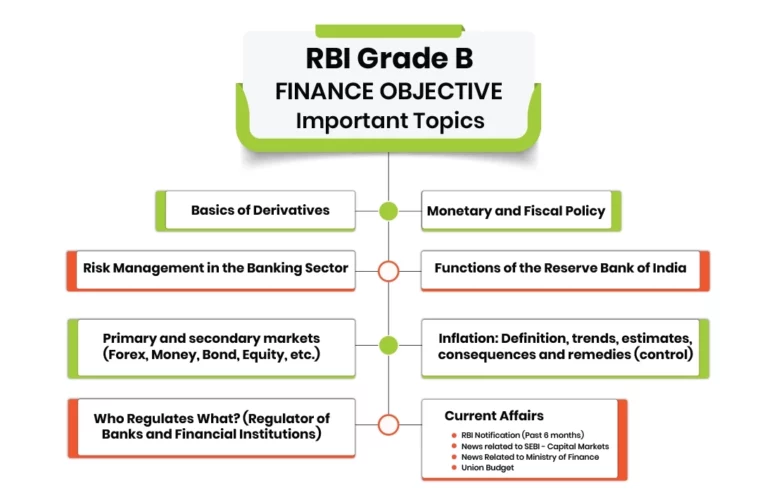
Finance (Objective)
Here are the most important topics for finance objective:
- Primary and secondary markets (Forex, Money, Bond, Equity, etc.), functions, instruments, and recent developments.
- Risk Management in the Banking Sector
- Inflation: Definition, trends, estimates, consequences and remedies (control): WPI- CPI – components and trends; striking a balance between inflation and growth through monetary and fiscal policies
- Basics of Derivatives
- Functions of the Reserve Bank of India
- Monetary and Fiscal Policy
- Who Regulates What? (Regulator of Banks and Financial Institutions)
- Current Affairs:
- RBI Notification (Past 6 months)
- News related to SEBI – Capital Markets
- News Related to Ministry of Finance
- Union Budget
Finance (Subjective)
Here are some of the important chapters based on the previous years’ question papers analysis:
- Recent Developments in the Global Financial System and its Impact on Indian Financial System
- Global financial markets and International Banking – broad trends and latest developments
- Financial Inclusion
- Alternate source of finance, private and social cost-benefit, Public-Private Partnership
- Corporate Governance in the Banking Sector, the role of e-governance in addressing issues of corruption and inefficiency in the government sector.
Management (Objective)
Here are the most important topics for management objective:
- Motivation
- Leadership
- Communication
- General Management
- Emotional Intelligence
- Personality and Perception
- Conflict
- Organizational Change and Reinforcement
- Corporate Governance
- Ethics
Management (Subjective)
Here are some of the important chapters based on the previous years’ question papers analysis:
- Leadership
- Communication
- General Management
- Organizational Change & Reinforcement
- Corporate Governance
- Ethics
Check out the video explaining the important topics and chapters of Finance and Management for the RBI Grade B exam.
After understanding the important topics, let’s take a look at their difficulty level.
RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management Difficulty Level
Below is the objective and subjective difficulty level of RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management:
Finance and Management Phase 2 Objective Difficulty Level
The table below contains the year-wise distribution of easy, moderate, and difficult questions out of the total number of objective finance and management questions from 2019 to 2023. Understanding the difficulty level of questions helps you tailor your approach, prioritise topics, and fine-tune your preparation strategy.
| Finance and Management Difficulty Level Phase 2 (Objective) | |||||
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | 2019 | ||
| Total Questions | 30 | 30 | 30 | 75 | |
| Difficulty Level | Easy | 25 | 16 | 23 | 51 |
| Moderate | 5 | 11 | 6 | 13 | |
| Difficult | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | |
Finance and Management Phase 2 Subjective Difficulty Level
The table below contains the year-wise distribution of easy, moderate, and difficult questions out of the total number of subjective finance and management questions from 2021 to 2023. Understanding the difficulty level of descriptive questions helps you tailor your answer writing approach to fine-tune your preparation strategy.
| Finance and Management Difficulty Level Phase 2 (Subjective) | ||||
| 2023 | 2022 | 2021 | ||
| Total Questions | 6 | 6 | 6 | |
| Difficulty Level | Easy | 1 | 2 | 5 |
| Moderate | 5 | 4 | 1 | |
| Difficult | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
After getting familiar with the difficulty level, let’s understand the type of Finance and Management questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2 exam.
Types of Finance and Management Questions
Understanding the types of questions helps you identify the level and formats of Finance and Management questions asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2. It ensures that you are thoroughly prepared for all FM question types encountered in the exam. Below, we have explained the type of questions asked from each important topic of Finance and Management in the RBI Grade B Phase 2:
Finance (Objective)
Below are the types of objective Finance questions asked in the exam.
1. Primary and Secondary Markets (Forex, Money, Bond, Equity, etc.), functions, instruments, and recent developments.
Question 1: Choose the right statement about Primary and Secondary Markets?
- Primary Markets Cater to new Issues of Capital whereas Secondary Markets Caters to new Issues of Debt
- Primary Markets Cater to new issues of Capital whereas Secondary Markets Caters to transfer of ownership among the existing Owners or from existing to new Owners
- Primary Markets Cater to transfer of ownership among existing owners whereas secondary markets cater to transfer from ownership from existing to new Owners
- Primary Markets Cater to new Issues of Debt whereas Secondary Markets Caters to new Issues of Equity
- None of the Above
Question 2: If 1:1 Bonus issue is given then what would be the impact on Tangible Net worth?
- Tangible Net Worth would increase
- Tangible Net Worth would Decrease
- Tangible Net Worth would increase/Decrease depending on how the bonus issue is financed
- Tangible Net Worth would remain the same
2. Risk Management in the Banking Sector
Question 1: In Banking Sector, Market risk arises mainly due to _____________ ?
- Political factors
- External factors
- Natural calamities
- Internal factors
- None of the above
Question 2: Operational Risk in an organization arises from which of the following reasons?
- New regulatory norms
- Inadequate internal control process
- Inadequate external control process
- Strict internal control process
- None of the above
3. Inflation: Definition, trends, estimates, consequences and remedies (control): WPI- CPI – components and trends; striking a balance between inflation and growth through monetary and fiscal policies
Question 1: Which of the following phenomenon includes High inflation & high unemployment?
- Hyperinflation
- Deflation
- Disinflation
- Stagflation
- None of the above
Question 2: The base year for the Revised series of WPI is _________________?
- 2010-11
- 2011-12
- 2013-2014
- 2009-2010
- 2012-2013
4. Basics of Derivatives
Question 1: Derivatives are financial instruments to hedge risk. It derives its value from which of the following?
- Exchange determined
- Fixed by SEBI
- Underlying
- Market determined
- None of the above
Question 2: Which of the following risk can be eliminated by derivatives?
- Market risk
- Systematic risk
- Systemic risk
- Interest rate risk
- None of the above
5. Functions of the Reserve Bank of India
Question 1: Which of the following institution is also known as lender of last resort?
- SBI
- HDFC Bank
- RBI
- NABARD
- ICICI Bank
Question 2: The Reserve Bank of India (RBI) pays interest on the CRR balance to the banks at _______?
- 2% above repo rate
- Repo rate
- 2% below bank rate
- Bank Rate
- No interest is paid on the CRR balance
6. Monetary and Fiscal Policy
Question 1: Who is responsible for conducting monetary policy in India?
- Ministry of Finance
- Department of Financial Services
- Department of Economic Affairs
- Reserve Bank of India
- None of the above
Question 2: Which among the following is/are tasks of Monetary Policy Committee?
a) Devise policy rate while maintaining price stability
b) Fixing the benchmark policy rate (repo rate)
c) Containing inflation within the specified target level
d) Devising mechanism for implementing fiscal policy
Select the correct answer from following options:
- Only b
- Only c
- Only a, c and d
- Only a, b and c
- All are correct
7. Who Regulates What? (Regulator of Banks and Financial Institutions)
Question 2: Udaymi Mitra Portal launched by SIDBI is for________________ ?
- Large Scale Industries
- Small and Medium Enterprises
- Rural Industry
- Automotive Industry
- None of the above
Question 2: Which of the following statement is/are true?
- SEBI is the regulator of commodity markets
- RBI is the regulator of NBFCs
- SEBI is the regulator of Capital Market
Which of the above statements are true ?
- Only I
- I and III only
- I, II and III
- II and III only
- None of the above
8. Current Affairs: RBI Notification (Past 6 months), News related to SEBI – Capital Markets, News Related to Ministry of Finance, Union Budget
Question 1: The Union government, in consultation with the RBI, fixes the inflation target for the central bank every five years. The Upper Tolerance level of Inflation is ____________ and in case of breach of the upper tolerance for ___________ quarters the report has to be submitted by RBI.
A. 4.0%, three consecutive quarters
B. 5.0%, two consecutive quarters
C. 6.0%, two consecutive quarters
D. 6.0%, three consecutive quarters
E. 5.0%, three consecutive quarters
Management (Objective)
Below are the types of objective Management questions asked in the exam.
1. Motivation
Read the following paragraph and answer the question that follows.
Motivation is the driving force that compels individuals to act and pursue goals, stemming from internal desires or external incentives. It energizes behavior, directing efforts toward achieving objectives and satisfying needs, influencing performance and satisfaction in various aspects of life.
Two eminent contributors to the field of motivation are Abraham Maslow and David McClelland. They have identified specific workplace motivational needs. In this context, David McClelland proposed ______”X”______ motivating elements, while Maslow presented the hierarchical structure of the need pyramid. Their seminal work has significantly advanced the understanding of human motivation in organizational settings.
Question 1: Identify “X” from the following given options.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- None of the above
Read the following paragraph and answer the question that follows.
Motivation is the driving force that compels individuals to act and pursue goals, stemming from internal desires or external incentives. It energizes behavior, directing efforts toward achieving objectives and satisfying needs, influencing performance and satisfaction in various aspects of life.
Two eminent contributors to the field of motivation are Abraham Maslow and David McClelland. They have identified specific workplace motivational needs. In this context, David McClelland proposed ______”X”______ motivating elements, while Maslow presented the hierarchical structure of the need pyramid. Their seminal work has significantly advanced the understanding of human motivation in organizational settings.
Question 1: With regards of the above paragraph, if an employee is currently at the Physiological needs, then what will be the highest level as per Maslow motivational theory.
- Safety Needs
- Security Needs
- Belonginess Needs
- Self Esteem Needs
- Self-Actualization Needs
2. Leadership
Question 1: The managerial grid theory on which the Reddin model is based, was given by which of the following personalities?
- Tannenbaum and Schmidt
- Blake and Mouton
- Huneryager and Heckman
- Hersey & Blanchard
- None of the above
Read the following paragraph and answer the question that follows
Leadership is the process of guiding and influencing individuals or a group to achieve shared goals. Effective leaders inspire and motivate others, foster collaboration, and make strategic decisions. Leadership involves traits like communication, empathy, vision, and adaptability, empowering people to realize their potential and achieve collective success.
Kurt Lewin, a psychologist, made significant contributions to the study of leadership through his research on group dynamics and social psychology.
Question 1: Which of the following are the three leadership styles introduced by Kurt Lewin in 1930?
- Autocratic, Democratic, and Equity
- Autocratic, Democratic, and Laissez-faire.
- Autocratic, Delegative, and Equity
- Power, Democratic, and Equity
- Autocratic, Democratic, and Supportive
3. Communication
Directions: Read the following Paragraph and answer the questions that follow.
Rohan’s career journey was full of changes, trying out different roles. However, poor communication always held him back. Despite his skills, he felt the need to conquer this obstacle for true success. Like Rohan, many people face multiple barriers to the communication process, some of them are listed below –
- Misunderstanding due to translation error caused by to lack of proficiency of translator in both languages.
- Lack of confidence of subordinates to communicate and give feedback to superiors.
- Rules and regulations hindering the communication and Complexity in Organizational structure
- Lack of time due to a pre-occupied mind
Lastly, Rohan can improve his communication skills through several steps. Firstly, he should actively listen to others and be open to feedback. Practicing clear and concise expression will help him articulate his ideas better.
Question 1: With regards to the above-mentioned passage, which of the following is/are example of personal barriers in the communication process.
- Only A
- Only B
- Only C and B
- Only A, B and C
- Only B and D
Question 2: Identify the barriers of communication, wherein the person (Sender or Receiver) is unable to translate the language in the required manner.
- Personal Barriers
- Semantic Barriers
- Organizational Barriers
- Emotional Barriers
- Psychological barriers
4. General Management
Question 1: Which of the following theory suggests to make communication in an organization, based on Hierarchy and communication should be highly structured and it should be formalized too?
- Frederick Taylor – Theory of Scientific Management
- Henri Fayol – Administrative Management Theory
- Max Weber – Bureaucratic Theory of Management
- Elton Mayo – Behavioral Theory of Management
- None of the above
Question 2: Under which method, the communication flows from top to bottom in an Organization?
- Scalar Chain
- Vertical command
- Line of Authority
- Communication line
- None of Above
5. Emotional Intelligence
Question 1: According to Johari Window, Quadrant known to self but not known to others is called as_____________?
- Open
- Blind
- Hidden
- Unknown
- None of above
Question 2: In the field of Management, ____________________ describes the difference between true and exposed emotions.
- Perception Defense
- Emotional Intelligence
- Cognitive Dissonance
- Emotional dissonance
- Emotional Management
6. Personality and Perception
Question 1: In an organization, an employee is reliable, dependable, goal-oriented, and cooperative. Which of the following personality of the employee is reflected as per Big Five Personality Model?
- Agreeableness
- Conscientiousness
- Emotional Stability
- Extroversion
- None of the above
Question 2: As per OCEAN model, if a person is organized, self-disciplined and he or she is achievement oriented, then which of the following personality trait can be associated to him or her?
- Openness
- Extraversion
- Agreeableness
- Conscientiousness
- Neuroticism
7. Conflict
Question 1: Bargaining technique wherein employees’ bargain for bonus which is completely related to productivity, such bargaining is called as ____________________?
- Collective Bargaining
- Composite Bargaining
- Co-operative or Integrative Bargaining
- Conjunctive or Distributive Bargaining
- Productivity Bargaining
8. Organizational Change and Reinforcement
Question 1: __________refers to the actions in which a company or business alters a major component of its organization, such as its culture, the underlying technologies or infrastructure it uses to operate, or its internal processes.
What is the name of the second stage of Kurt Lewin’s organizational change model?
- Change
- Development
- Resistance
- Compliance
- None of the above
Question 2: In which stage of the Lewin Change Management Model, we see reinforcement strategies practiced by the management?
- Change
- Un-freezing
- Re-Freezing
- Dynamic
- None of the above
9. Corporate Governance
Read the following Paragraph and answer the questions which follows
Corporate social responsibility (CSR) is a self-regulating business model that helps a company be socially accountable to itself, its stakeholders, and the public. By practicing corporate social responsibility, also called corporate citizenship, companies can be conscious of the kind of impact they are having on all aspects of society, including economic, social, and environmental.
To engage in CSR means that, in the ordinary course of business, a company is operating in ways that enhance society and the environment instead of contributing negatively to them.
According to SEBI, Companies eligible for CSR shall constitute a Corporate Social Responsibility Committee of the Board consisting of _____”A”_______ or more directors, out of which at least ______”B”_______ shall be an independent director.
Question 1: Identify “B” from the following given options.
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- None of the above
Question 1: Identify the theory of corporate governance, which is based on the perception that a corporation for its effective function has to forge a number of relations with different people/institutions including suppliers, consumers, employees, government.
- Steward Ship Theory
- Stakeholder Theory
- Agency Theory
- Feedback Theory
- None of the above
10. Ethics
Question 1: Which of the following theories of ethics, focusses on consequences of greater good and evil?
- Teleological Theory of Ethics
- Deontological Theory of Ethics
- Virtue Ethics
- Ethics-Justice Theory
- None of the above
Question 2: Generally, _____________ is the principle which focusses on the kind of value which displaces concerns of others.
- Distribution
- Justice
- Right
- Entitlements
- Care
Finance and Management (Subjective)
Below are the types of subjective Finance and Management questions asked in the exam.
Question 1: What is Open Network for Digital Commerce (ONDC)? How it will beat other e-commerce giants like Amazon and Flipkart (400 words, 10 marks)
Question 2: What is a code of conduct? How it is implemented in an organization (400 words, 10 marks)
Question 3: RBI has Allowed Pre-Sanctioned Credit Lines Via UPI. How is it a step towards financial inclusion? (400 words, 10 marks)
Question 4: What is the contribution of Henry Fayol in the field of management? Also, explain fourteen principles of management as given by him? (600 words, 15 marks)
Question 5: Discuss the big-five model of personality. (600 words, 15 marks)
Question 6: Briefly explain the Retail direct scheme of the Reserve Bank of India (RBI)? (600 words, 15 marks)
Click here to Download the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management PYQs in PDF.
Now that you have understood the types of Finance and Management questions (Objective and Subjective) asked in the RBI Grade B Phase 2, let’s learn the important books to prepare for the exam.
Important Books for RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management
Here are the important books that can help you cover the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management syllabus.
| RBI Grade B Finance Books for Phase 2 Exam Preparation | |||
| Books | Author | Publisher | Buy Here |
| Principles of Practices of Banking | Macmillan Education | Macmillan Publishers India Pvt. Ltd. | Buy Online |
| Bank Financial Management | IIBF (Indian Institute of Banking and Finance) | Macmillan Publishers India Pvt. Ltd. | Buy Online |
| Financial Management | R.P. Rustagi | Taxmann Publications Private Limited | Buy Online |
Other Preparation Material
| RBI Grade B Management Books for Phase 2 Exam Preparation | |||
| Books | Author | Publisher | Buy Here |
| Principles and Practice of Management | L.M. Prasad | Sultan Chand & Sons | Buy Online |
| Organizational Behaviour | L.M. Prasad | Sultan Chand & Sons | Buy Online |
| Business Ethics and Corporate Governance | B.N Ghosh | McGraw Hill Education | Buy Online |
Other Preparation Material
Important Note: No current affairs are asked in the exam from the management section, so the above-mentioned RBI Grade B management books are sufficient for preparation.
Here is a video explaining books for RBI Grade B Finance and Management.
After getting familiar with the important books, let’s understand the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management preparation strategy.
How to Prepare for RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management
Follow these below-mentioned strategies to prepare for RBI Grade B Phase 2 Finance and Management:
1. Break the Finance and Management Syllabus
Finance and Management subjects consist of a maximum of 50 marks each. Here, achieving 40 to 45 marks in Management and 35 to 40 marks in Finance is possible if you prepare well for the exam.
2. Understand the Management Format
Management is divided into two parts: Objective and Subjective.
a. Objective
1. Read All Chapters
Although we have mentioned important chapters above in the article, it is important for you to read all the chapters mentioned in the RBI Grade B Phase 2 Management syllabus. If you are targeting 40 to 45 in Management, you can not take the risk of leaving any chapter.
2. Practice MCQs
You must practise as many MCQs as possible. It helps you identify your strengths and weaknesses across different topics, allowing you to improve in areas requiring more attention.
3. Practice Case Studies
Practise some case studies, as some questions were asked from case studies in the 2023 exam.
4. Revise
Please note that you must revise after completing 3 to 4 chapters to reinforce your understanding.
b. Subjective
1. Practice Writing Descriptive Answers from Object Topics
Easy questions are asked from the subjective section of Management. You don’t need to prepare separately for the descriptive part. You can practise the objective topics for your answer writing practice as questions are directly based on objective topics such as communication and corporate governance.
2. Give Examples in Your Writings
However, if you want to score well, you need to give some good examples in your descriptive answers. For e.g., when answering a question on conflict, avoid presenting generic theories. Instead, include real-life examples within an organisational context to enhance the depth and impact of your answer.
3. Re-Call
Just like revising objective sections, recalling the topics you’ve studied is crucial to retaining the information in your memory. This process helps retain the key concepts, ensuring you can easily incorporate them into your descriptive answers.
3. Understand the Finance Format
Finance is divided into two parts: Objective and Subjective.
a. Objective
1. Prioritise Essential Chapters
When preparing for the Finance objective, it’s vital to focus on crucial topics first, as mentioned above in the article. Moreover, if time permits, you can cover the remaining topics.
2. Stay Updated on Current Affairs
Stay well-informed with Finance current affairs by referring to RBI notifications, supplemented by SEBI and Ministry of Finance notifications for comprehensive coverage.
3. Practice Numericals
Please note that, in the past two years, no numerical questions have been asked in the exam. However, RBI has added some new chapters to the Grade B Phase 2 syllabus, such as income statements, balance sheets, ratios, etc. Therefore, incorporating numerical practice is advisable for a well-rounded preparation.
4. Revise
Please note that you must revise after completing 3 to 4 chapters to reinforce your understanding.
b. Subjective
1. Practice Current Affairs Questions
Practise your descriptive writing answers from the topics mentioned above in the article. Additionally, integrate current affairs topics into your practice, covering areas like.
- Financial Stability Report (FSR)
- RBI Annual Report
- Reports in Trends in Banking Industries
- Union Budget
- Economic Surveys
Here is a video of the Finance and Management syllabus preparation strategy for RBI Grade B exam.

Conclusion
In this article, we have covered the detailed RBI Grade B Phase 2 syllabus for each subject. Our coverage includes insightful trend analysis, important topics, recommended sources for preparation, types of questions, and strategies to effectively prepare for each subject. Gaining a deep understanding of the syllabus allows you to create a tailored preparation strategy to crack the RBI Grade B Phase 2.
FAQs
No, the RBI Grade B syllabus is different from the NABARD Grade A exam. While there are some similarities between the RBI Grade B and NABARD Grade A syllabus, they also have distinct differences. Both exams cover general awareness, economic and social issues, and finance-related subjects. However, the depth, focus areas, and specific topics may vary.
Prioritise subjects based on your strengths and weaknesses. Create a study schedule allocating dedicated time to each subject daily.
Focus on RBI notifications, SEBI notifications, and Ministry of Finance notifications to stay updated on Finance current affairs.
While the core structure of the RBI Grade B Phase 2 syllabus remains the same, the topics are subject to changes. RBI recently updated the syllabus of the RBI Grade B Phase 2 in 2023. Read our article “RBI Grade B 2024 Pattern and Syllabus” to understand the old and new syllabus in detail.